Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC) enables access management for Azure resources. Using Azure RBAC, you can segregate duties within your team and grant only the amount of access to users, groups, and applications that they need to perform their jobs. You can grant role-based access to users using the Azure portal, Azure Command-Line tools, or Azure Management APIs.
Roles in Automation accounts
In Azure Automation, access is granted by assigning the appropriate Azure role to users, groups, and applications at the Automation account scope. Following are the built-in roles supported by an Automation account:
| Role | Description |
|---|---|
| Owner | The Owner role allows access to all resources and actions within an Automation account including providing access to other users, groups, and applications to manage the Automation account. |
| Contributor | The Contributor role allows you to manage everything except modifying other user’s access permissions to an Automation account. |
| Reader | The Reader role allows you to view all the resources in an Automation account but can’t make any changes. |
| Automation Contributor | The Automation Contributor role allows you to manage all resources in the Automation account, except modifying other user’s access permissions to an Automation account. |
| Automation Operator | The Automation Operator role allows you to view runbook name and properties and to create and manage jobs for all runbooks in an Automation account. This role is helpful if you want to protect your Automation account resources like credentials assets and runbooks from being viewed or modified but still allow members of your organization to execute these runbooks. |
| Automation Job Operator | The Automation Job Operator role allows you to create and manage jobs for all runbooks in an Automation account. |
| Automation Runbook Operator | The Automation Runbook Operator role allows you to view a runbook’s name and properties. |
| Log Analytics Contributor | The Log Analytics Contributor role allows you to read all monitoring data and edit monitoring settings. Editing monitoring settings includes adding the VM extension to VMs, reading storage account keys to be able to configure collection of logs from Azure storage, creating and configuring Automation accounts, adding Azure Automation features, and configuring Azure diagnostics on all Azure resources. |
| Log Analytics Reader | The Log Analytics Reader role allows you to view and search all monitoring data as well as view monitoring settings. This includes viewing the configuration of Azure diagnostics on all Azure resources. |
| Monitoring Contributor | The Monitoring Contributor role allows you to read all monitoring data and update monitoring settings. |
| Monitoring Reader | The Monitoring Reader role allows you to read all monitoring data. |
| User Access Administrator | The User Access Administrator role allows you to manage user access to Azure Automation accounts. |
Role permissions
The following tables describe the specific permissions given to each role. This can include Actions, which give permissions, and Not Actions, which restrict them.
Owner
An Owner can manage everything, including access. The following table shows the permissions granted for the role:
| Actions | Description |
|---|---|
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/* | Create and manage resources of all types. |
Contributor
A Contributor can manage everything except access. The following table shows the permissions granted and denied for the role:
| Actions | Description |
|---|---|
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/* | Create and manage resources of all types |
| Not Actions | |
| Microsoft.Authorization/*/Delete | Delete roles and role assignments. |
| Microsoft.Authorization/*/Write | Create roles and role assignments. |
| Microsoft.Authorization/elevateAccess/Action | Denies the ability to create a User Access Administrator. |
Reader
Note
We have recently made a change in the built-in Reader role permission for the Automation account. Learn more
A Reader can view all the resources in an Automation account but can’t make any changes.
| Actions | Description |
|---|---|
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/read | View all resources in an Automation account. |
Automation Contributor
An Automation Contributor can manage all resources in the Automation account except access. The following table shows the permissions granted for the role:
| Actions | Description |
|---|---|
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/* | Create and manage resources of all types. |
| Microsoft.Authorization/*/read | Read roles and role assignments. |
| Microsoft.Resources/deployments/* | Create and manage resource group deployments. |
| Microsoft.Resources/subscriptions/resourceGroups/read | Read resource group deployments. |
| Microsoft.Support/* | Create and manage support tickets. |
| Microsoft.Insights/ActionGroups/* | Read/write/delete action groups. |
| Microsoft.Insights/ActivityLogAlerts/* | Read/write/delete activity log alerts. |
| Microsoft.Insights/diagnosticSettings/* | Read/write/delete diagnostic settings. |
| Microsoft.Insights/MetricAlerts/* | Read/write/delete near real-time metric alerts. |
| Microsoft.Insights/ScheduledQueryRules/* | Read/write/delete log alerts in Azure Monitor. |
| Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/sharedKeys/action | List keys for a Log Analytics workspace |
Note
The Automation Contributor role can be used to access any resource using the managed identity, if appropriate permissions are set on the target resource, or using a Run As account. An Automation Run As account are by default, configured with Contributor rights on the subscription. Follow the principal of least privilege and carefully assign permissions only required to execute your runbook. For example, if the Automation account is only required to start or stop an Azure VM, then the permissions assigned to the Run As account or managed identity needs to be only for starting or stopping the VM. Similarly, if a runbook is reading from blob storage, then assign read only permissions.
When assigning permissions, it is recommended to use Azure role based access control (RBAC) assigned to a managed identity. Review our best approach recommendations for using a system or user-assigned managed identity, including management and governance during its lifetime.
Automation Operator
An Automation Operator is able to create and manage jobs, and read runbook names and properties for all runbooks in an Automation account.
Note
If you want to control operator access to individual runbooks then don’t set this role. Instead use the Automation Job Operator and Automation Runbook Operator roles in combination.
The following table shows the permissions granted for the role:
| Actions | Description |
|---|---|
| Microsoft.Authorization/*/read | Read authorization. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/hybridRunbookWorkerGroups/read | Read Hybrid Runbook Worker Resources. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobs/read | List jobs of the runbook. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobs/resume/action | Resume a job that is paused. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobs/stop/action | Cancel a job in progress. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobs/streams/read | Read the Job Streams and Output. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobs/output/read | Get the Output of a job. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobs/suspend/action | Pause a job in progress. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobs/write | Create jobs. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobSchedules/read | Get an Azure Automation job schedule. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobSchedules/write | Create an Azure Automation job schedule. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/linkedWorkspace/read | Get the workspace linked to the Automation account. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/read | Get an Azure Automation account. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/runbooks/read | Get an Azure Automation runbook. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/schedules/read | Get an Azure Automation schedule asset. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/schedules/write | Create or update an Azure Automation schedule asset. |
| Microsoft.Resources/subscriptions/resourceGroups/read | Read roles and role assignments. |
| Microsoft.Resources/deployments/* | Create and manage resource group deployments. |
| Microsoft.Insights/alertRules/* | Create and manage alert rules. |
| Microsoft.Support/* | Create and manage support tickets. |
| Microsoft.ResourceHealth/availabilityStatuses/read | Gets the availability statuses for all resources in the specified scope. |
Automation Job Operator
An Automation Job Operator role is granted at the Automation account scope. This allows the operator permissions to create and manage jobs for all runbooks in the account. If the Job Operator role is granted read permissions on the resource group containing the Automation account, members of the role have the ability to start runbooks. However, they don’t have the ability to create, edit, or delete them.
The following table shows the permissions granted for the role:
| Actions | Description |
|---|---|
| Microsoft.Authorization/*/read | Read authorization. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobs/read | List jobs of the runbook. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobs/resume/action | Resume a job that is paused. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobs/stop/action | Cancel a job in progress. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobs/streams/read | Read the Job Streams and Output. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobs/suspend/action | Pause a job in progress. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobs/write | Create jobs. |
| Microsoft.Resources/subscriptions/resourceGroups/read | Read roles and role assignments. |
| Microsoft.Resources/deployments/* | Create and manage resource group deployments. |
| Microsoft.Insights/alertRules/* | Create and manage alert rules. |
| Microsoft.Support/* | Create and manage support tickets. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/hybridRunbookWorkerGroups/read | Reads a Hybrid Runbook Worker Group. |
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobs/output/read | Gets the output of a job. |
Automation Runbook Operator
An Automation Runbook Operator role is granted at the Runbook scope. An Automation Runbook Operator can view the runbook’s name and properties. This role combined with the Automation Job Operator role enables the operator to also create and manage jobs for the runbook. The following table shows the permissions granted for the role:
| Actions | Description |
|---|---|
| Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/runbooks/read | List the runbooks. |
| Microsoft.Authorization/*/read | Read authorization. |
| Microsoft.Resources/subscriptions/resourceGroups/read | Read roles and role assignments. |
| Microsoft.Resources/deployments/* | Create and manage resource group deployments. |
| Microsoft.Insights/alertRules/* | Create and manage alert rules. |
| Microsoft.Support/* | Create and manage support tickets. |
Log Analytics Contributor
A Log Analytics Contributor can read all monitoring data and edit monitoring settings. Editing monitoring settings includes adding the VM extension to VMs; reading storage account keys to be able to configure collection of logs from Azure Storage; creating and configuring Automation accounts; adding features; and configuring Azure diagnostics on all Azure resources. The following table shows the permissions granted for the role:
| Actions | Description |
|---|---|
| */read | Read resources of all types, except secrets. |
| Microsoft.ClassicCompute/virtualMachines/extensions/* | Create and manage virtual machine extensions. |
| Microsoft.ClassicStorage/storageAccounts/listKeys/action | List classic storage account keys. |
| Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/extensions/* | Create and manage classic virtual machine extensions. |
| Microsoft.Insights/alertRules/* | Read/write/delete alert rules. |
| Microsoft.Insights/diagnosticSettings/* | Read/write/delete diagnostic settings. |
| Microsoft.OperationalInsights/* | Manage Azure Monitor logs. |
| Microsoft.OperationsManagement/* | Manage Azure Automation features in workspaces. |
| Microsoft.Resources/deployments/* | Create and manage resource group deployments. |
| Microsoft.Resources/subscriptions/resourcegroups/deployments/* | Create and manage resource group deployments. |
| Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/listKeys/action | List storage account keys. |
| Microsoft.Support/* | Create and manage support tickets. |
| Microsoft.HybridCompute/machines/extensions/write | Installs or Updates an Azure Arc extensions. |
Log Analytics Reader
A Log Analytics Reader can view and search all monitoring data as well as and view monitoring settings, including viewing the configuration of Azure diagnostics on all Azure resources. The following table shows the permissions granted or denied for the role:
| Actions | Description |
|---|---|
| */read | Read resources of all types, except secrets. |
| Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/analytics/query/action | Manage queries in Azure Monitor logs. |
| Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/search/action | Search Azure Monitor log data. |
| Microsoft.Support/* | Create and manage support tickets. |
| Not Actions | |
| Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/sharedKeys/read | Not able to read the shared access keys. |
Monitoring Contributor
A Monitoring Contributor can read all monitoring data and update monitoring settings. The following table shows the permissions granted for the role:
| Actions | Description |
|---|---|
| */read | Read resources of all types, except secrets. |
| Microsoft.AlertsManagement/alerts/* | Manage Alerts. |
| Microsoft.AlertsManagement/alertsSummary/* | Manage the Alert dashboard. |
| Microsoft.Insights/AlertRules/* | Manage alert rules. |
| Microsoft.Insights/components/* | Manage Application Insights components. |
| Microsoft.Insights/DiagnosticSettings/* | Manage diagnostic settings. |
| Microsoft.Insights/eventtypes/* | List Activity Log events (management events) in a subscription. This permission is applicable to both programmatic and portal access to the Activity Log. |
| Microsoft.Insights/LogDefinitions/* | This permission is necessary for users who need access to Activity Logs via the portal. List log categories in Activity Log. |
| Microsoft.Insights/MetricDefinitions/* | Read metric definitions (list of available metric types for a resource). |
| Microsoft.Insights/Metrics/* | Read metrics for a resource. |
| Microsoft.Insights/Register/Action | Register the Microsoft.Insights provider. |
| Microsoft.Insights/webtests/* | Manage Application Insights web tests. |
| Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/intelligencepacks/* | Manage Azure Monitor logs solution packs. |
| Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/savedSearches/* | Manage Azure Monitor logs saved searches. |
| Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/search/action | Search Log Analytics workspaces. |
| Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/sharedKeys/action | List keys for a Log Analytics workspace. |
| Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/storageinsightconfigs/* | Manage Azure Monitor logs storage insight configurations. |
| Microsoft.Support/* | Create and manage support tickets. |
| Microsoft.WorkloadMonitor/workloads/* | Manage Workloads. |
Monitoring Reader
A Monitoring Reader can read all monitoring data. The following table shows the permissions granted for the role:
| Actions | Description |
|---|---|
| */read | Read resources of all types, except secrets. |
| Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/search/action | Search Log Analytics workspaces. |
| Microsoft.Support/* | Create and manage support tickets |
User Access Administrator
A User Access Administrator can manage user access to Azure resources. The following table shows the permissions granted for the role:
| Actions | Description |
|---|---|
| */read | Read all resources |
| Microsoft.Authorization/* | Manage authorization |
| Microsoft.Support/* | Create and manage support tickets |
Reader role access permissions
Important
To strengthen the overall Azure Automation security posture, the built-in RBAC Reader would not have access to Automation account keys through the API call – GET /AUTOMATIONACCOUNTS/AGENTREGISTRATIONINFORMATION.
The Built-in Reader role for the Automation Account can’t use the API – GET /AUTOMATIONACCOUNTS/AGENTREGISTRATIONINFORMATION to fetch the Automation Account keys. This is a high privilege operation providing sensitive information that could pose a security risk of an unwanted malicious actor with low privileges who can get access to automation account keys and can perform actions with elevated privilege level.
To access the API – GET /AUTOMATIONACCOUNTS/AGENTREGISTRATIONINFORMATION, we recommend that you switch to the built-in roles like Owner, Contributor or Automation Contributor to access the Automation account keys. These roles, by default, will have the listKeys permission. As a best practice, we recommend that you create a custom role with limited permissions to access the Automation account keys. For a custom role, you need to add Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/listKeys/action permission to the role definition. Learn more about how to create custom role from the Azure portal.
Feature setup permissions
The following sections describe the minimum required permissions needed for enabling the Update Management and Change Tracking and Inventory features.
Permissions for enabling Update Management and Change Tracking and Inventory from a VM
| Action | Permission | Minimum scope |
|---|---|---|
| Write new deployment | Microsoft.Resources/deployments/* | Subscription |
| Write new resource group | Microsoft.Resources/subscriptions/resourceGroups/write | Subscription |
| Create new default Workspace | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/write | Resource group |
| Create new Account | Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/write | Resource group |
| Link workspace and account | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/write Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/read | Workspace Automation account |
| Create MMA extension | Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/write | Virtual Machine |
| Create saved search | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/write | Workspace |
| Create scope config | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/write | Workspace |
| Onboarding state check – Read workspace | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/read | Workspace |
| Onboarding state check – Read linked workspace property of account | Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/read | Automation account |
| Onboarding state check – Read solution | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/intelligencepacks/read | Solution |
| Onboarding state check – Read VM | Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/read | Virtual Machine |
| Onboarding state check – Read account | Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/read | Automation account |
| Onboarding workspace check for VM1 | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/read | Subscription |
| Register the Log Analytics provider | Microsoft.Insights/register/action | Subscription |
1 This permission is needed to enable features through the VM portal experience.
Permissions for enabling Update Management and Change Tracking and Inventory from an Automation account
| Action | Permission | Minimum Scope |
|---|---|---|
| Create new deployment | Microsoft.Resources/deployments/* | Subscription |
| Create new resource group | Microsoft.Resources/subscriptions/resourceGroups/write | Subscription |
| AutomationOnboarding blade – Create new workspace | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/write | Resource group |
| AutomationOnboarding blade – read linked workspace | Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/read | Automation account |
| AutomationOnboarding blade – read solution | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/intelligencepacks/read | Solution |
| AutomationOnboarding blade – read workspace | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/intelligencepacks/read | Workspace |
| Create link for workspace and Account | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/write | Workspace |
| Write account for shoebox | Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/write | Account |
| Create/edit saved search | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/write | Workspace |
| Create/edit scope config | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/write | Workspace |
| Register the Log Analytics provider | Microsoft.Insights/register/action | Subscription |
| Step 2 – Enable Multiple VMs | ||
| VMOnboarding blade – Create MMA extension | Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/write | Virtual Machine |
| Create / edit saved search | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/write | Workspace |
| Create / edit scope config | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/write | Workspace |
Manage Role permissions for Hybrid Worker Groups and Hybrid Workers
You can create Azure custom roles in Automation and grant the following permissions to Hybrid Worker Groups and Hybrid Workers:
- Extension-based Hybrid Runbook Worker
- Agent-based Windows Hybrid Runbook Worker
- Agent-based Linux Hybrid Runbook Worker
Update Management permissions
Update Management can be used to assess and schedule update deployments to machines in multiple subscriptions in the same Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant, or across tenants using Azure Lighthouse. The following table lists the permissions needed to manage update deployments.
| Resource | Role | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| Automation account | Virtual Machine Contributor | Resource Group for the account |
| Log Analytics workspace | Log Analytics Contributor | Log Analytics workspace |
| Log Analytics workspace | Log Analytics Reader | Subscription |
| Solution | Log Analytics Contributor | Solution |
| Virtual Machine | Virtual Machine Contributor | Virtual Machine |
| Actions on Virtual Machine | ||
| View history of update schedule execution (Software Update Configuration Machine Runs) | Reader | Automation account |
| Actions on virtual machine | Permission | |
| Create update schedule (Software Update Configurations) | Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/write | For static VM list and resource groups |
| Create update schedule (Software Update Configurations) | Microsoft.OperationalInsights/workspaces/analytics/query/action | For workspace resource ID when using non-Azure dynamic list. |
Note
When you use Update management, ensure that the execution policy for scripts is RemoteSigned.
Configure Azure RBAC for your Automation account
The following section shows you how to configure Azure RBAC on your Automation account through the Azure portal and PowerShell.
Configure Azure RBAC using the Azure portal
- Sign in to the Azure portal and open your Automation account from the Automation Accounts page.
- Select Access control (IAM) and select a role from the list of available roles. You can choose any of the available built-in roles that an Automation account supports or any custom role you might have defined. Assign the role to a user to which you want to give permissions.For detailed steps, see Assign Azure roles using the Azure portal. NoteYou can only set role-based access control at the Automation account scope and not at any resource below the Automation account.
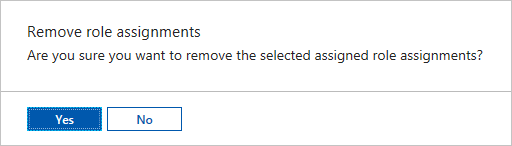
Remove role assignments from a user
You can remove the access permission for a user who isn’t managing the Automation account, or who no longer works for the organization. The following steps show how to remove the role assignments from a user. For detailed steps, see Remove Azure role assignments:
- Open Access control (IAM) at a scope, such as management group, subscription, resource group, or resource, where you want to remove access.
- Select the Role assignments tab to view all the role assignments at this scope.
- In the list of role assignments, add a checkmark next to the user with the role assignment you want to remove.
- Select Remove.
Configure Azure RBAC using PowerShell
You can also configure role-based access to an Automation account using the following Azure PowerShell cmdlets:
Get-AzRoleDefinition lists all Azure roles that are available in Azure Active Directory. You can use this cmdlet with the Name parameter to list all the actions that a specific role can perform.
Azure PowerShellCopyOpen Cloudshell
Get-AzRoleDefinition -Name 'Automation Operator'
The following is the example output:
Azure PowerShellCopy
Name : Automation Operator
Id : d3881f73-407a-4167-8283-e981cbba0404
IsCustom : False
Description : Automation Operators are able to start, stop, suspend, and resume jobs
Actions : {Microsoft.Authorization/*/read, Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobs/read, Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobs/resume/action,
Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/jobs/stop/action...}
NotActions : {}
AssignableScopes : {/}
Get-AzRoleAssignment lists Azure role assignments at the specified scope. Without any parameters, this cmdlet returns all the role assignments made under the subscription. Use the ExpandPrincipalGroups parameter to list access assignments for the specified user, as well as the groups that the user belongs to.
Example: Use the following cmdlet to list all the users and their roles within an Automation account.
Azure PowerShellCopyOpen Cloudshell
Get-AzRoleAssignment -Scope '/subscriptions/<SubscriptionID>/resourcegroups/<Resource Group Name>/Providers/Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/<Automation account name>'
The following is the example output:
PowerShellCopy
RoleAssignmentId : /subscriptions/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/resourceGroups/myResourceGroup/providers/Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/myAutomationAccount/provid
ers/Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments/cc594d39-ac10-46c4-9505-f182a355c41f
Scope : /subscriptions/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/resourceGroups/myResourceGroup/providers/Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/myAutomationAccount
DisplayName : admin@contoso.com
SignInName : admin@contoso.com
RoleDefinitionName : Automation Operator
RoleDefinitionId : d3881f73-407a-4167-8283-e981cbba0404
ObjectId : 15f26a47-812d-489a-8197-3d4853558347
ObjectType : User
Use New-AzRoleAssignment to assign access to users, groups, and applications to a particular scope.
Example: Use the following command to assign the “Automation Operator” role for a user in the Automation account scope.
Azure PowerShellCopyOpen Cloudshell
New-AzRoleAssignment -SignInName <sign-in Id of a user you wish to grant access> -RoleDefinitionName 'Automation operator' -Scope '/subscriptions/<SubscriptionID>/resourcegroups/<Resource Group Name>/Providers/Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/<Automation account name>'
The following is the example output:
Azure PowerShellCopy
RoleAssignmentId : /subscriptions/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/resourcegroups/myResourceGroup/Providers/Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/myAutomationAccount/provid
ers/Microsoft.Authorization/roleAssignments/25377770-561e-4496-8b4f-7cba1d6fa346
Scope : /subscriptions/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/resourcegroups/myResourceGroup/Providers/Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/myAutomationAccount
DisplayName : admin@contoso.com
SignInName : admin@contoso.com
RoleDefinitionName : Automation Operator
RoleDefinitionId : d3881f73-407a-4167-8283-e981cbba0404
ObjectId : f5ecbe87-1181-43d2-88d5-a8f5e9d8014e
ObjectType : User
Use Remove-AzRoleAssignment to remove access of a specified user, group, or application from a particular scope.
Example: Use the following command to remove the user from the Automation Operator role in the Automation account scope.
Azure PowerShellCopyOpen Cloudshell
Remove-AzRoleAssignment -SignInName <sign-in Id of a user you wish to remove> -RoleDefinitionName 'Automation Operator' -Scope '/subscriptions/<SubscriptionID>/resourcegroups/<Resource Group Name>/Providers/Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/<Automation account name>'
In the preceding example, replace sign-in ID of a user you wish to remove, SubscriptionID, Resource Group Name, and Automation account name with your account details. Choose yes when prompted to confirm before continuing to remove user role assignments.
User experience for Automation Operator role – Automation account
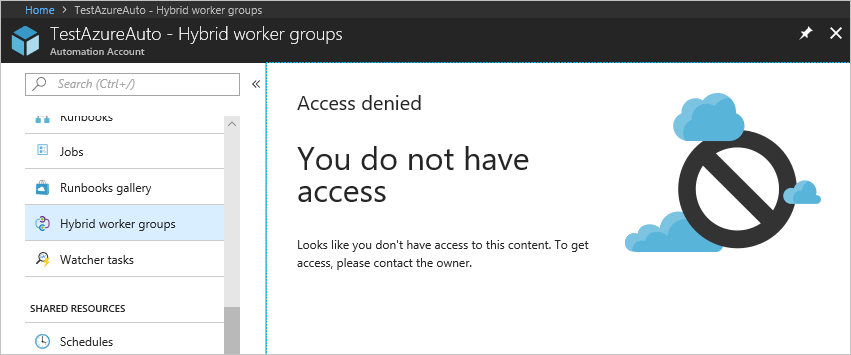
When a user assigned to the Automation Operator role on the Automation account scope views the Automation account to which he/she is assigned, the user can only view the list of runbooks, runbook jobs, and schedules created in the Automation account. This user can’t view the definitions of these items. The user can start, stop, suspend, resume, or schedule the runbook job. However, the user doesn’t have access to other Automation resources, such as configurations, Hybrid Runbook Worker groups, or DSC nodes.
Configure Azure RBAC for runbooks
Azure Automation allows you to assign Azure roles to specific runbooks. To do this, run the following script to add a user to a specific runbook. An Automation Account Administrator or a Tenant Administrator can run this script.
Azure PowerShellCopyOpen Cloudshell
$rgName = "<Resource Group Name>" # Resource Group name for the Automation account
$automationAccountName ="<Automation account name>" # Name of the Automation account
$rbName = "<Name of Runbook>" # Name of the runbook
$userId = "<User ObjectId>" # Azure Active Directory (AAD) user's ObjectId from the directory
# Gets the Automation account resource
$aa = Get-AzResource -ResourceGroupName $rgName -ResourceType "Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts" -ResourceName $automationAccountName
# Get the Runbook resource
$rb = Get-AzResource -ResourceGroupName $rgName -ResourceType "Microsoft.Automation/automationAccounts/runbooks" -ResourceName "$rbName"
# The Automation Job Operator role only needs to be run once per user.
New-AzRoleAssignment -ObjectId $userId -RoleDefinitionName "Automation Job Operator" -Scope $aa.ResourceId
# Adds the user to the Automation Runbook Operator role to the Runbook scope
New-AzRoleAssignment -ObjectId $userId -RoleDefinitionName "Automation Runbook Operator" -Scope $rb.ResourceId
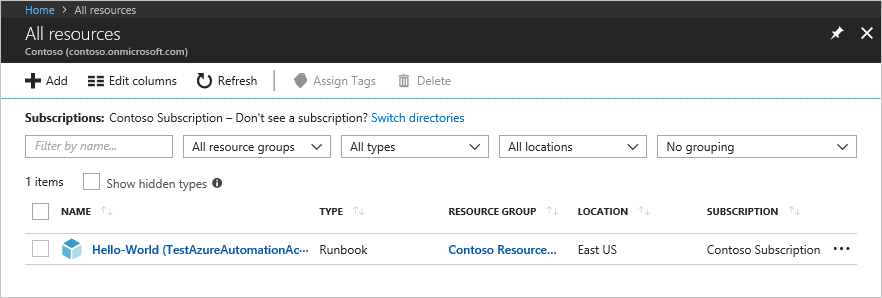
Once the script has run, have the user sign in to the Azure portal and select All Resources. In the list, the user can see the runbook for which he/she has been added as an Automation Runbook Operator.
User experience for Automation operator role – Runbook
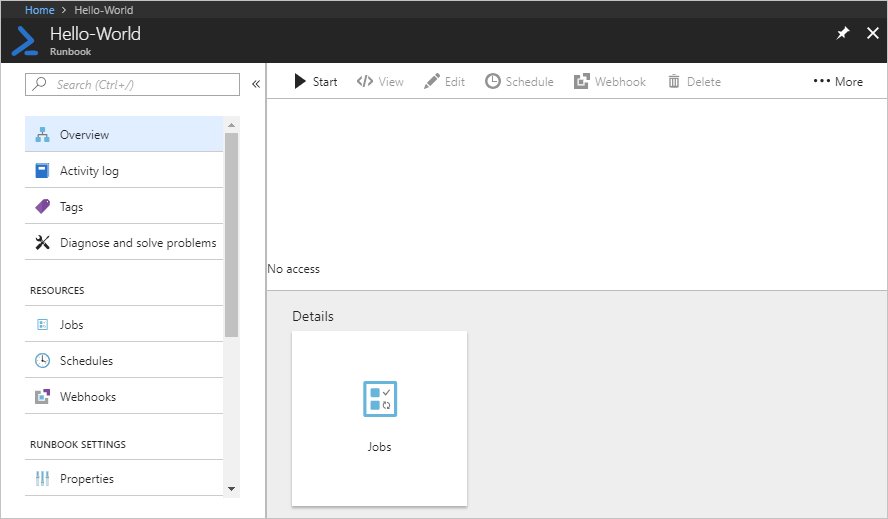
When a user assigned to the Automation Operator role on the Runbook scope views an assigned runbook, the user can only start the runbook and view the runbook jobs.
Next steps
- To learn about security guidelines, see Security best practices in Azure Automation.
- To find out more about Azure RBAC using PowerShell, see Add or remove Azure role assignments using Azure PowerShell.
- For details of the types of runbooks, see Azure Automation runbook types.
- To start a runbook, see Start a runbook in Azure Automation.